Last Updated on November 21, 2022

App lifecycle management (ALM) may seem complicated on the surface, but it is actually quite simple. ALM is the operation, from conception to termination, of software or an application. It allows for continuous development until its eventual discontinuation.
Apps may be created for a variety of reasons. These include providing customers with a purchasing platform or promoting the brand, as well as producing internal structural software to aid operations.
Apps can either be for customer (external) or employee (internal) use. Businesses create external apps and software with their customers in mind. This can help them to interact with the brand and buy their products.
Meanwhile, there are also internal apps for employee use. These can aid employee morale, productivity, and business organization in general. Companies use this type of management system to improve the efficiency of their software usage. It is not a quick process, and businesses need to put in work and investment to achieve the desired outcome.
Using ALM is one of the best options available when it comes to introducing new systems and apps. This is particularly important in our modern world. Competition is more fierce than ever. New technological solutions are being developed all the time, for all industries.
Below is an explanation of the five key stages of ALM. Thereafter, we will go through the possible advantages for your business.
The Five Key Stages of ALM
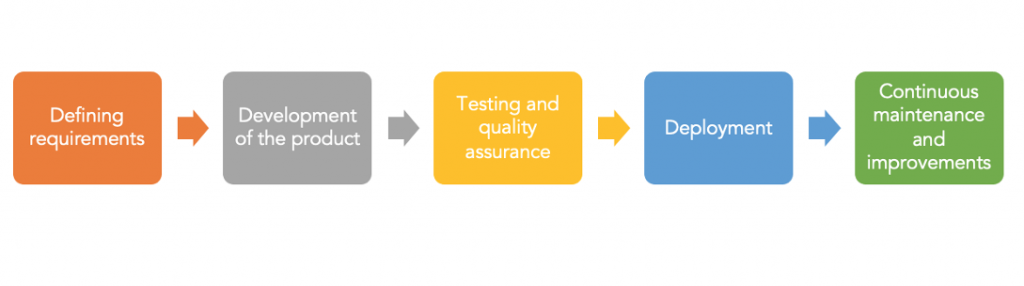
1. Defining requirements
Before starting any project, it is important to define your objectives. This helps to direct the operation and gives the business a chance to monitor the app’s future data and success in line with these. This helps when it comes to adjusting the app to better suit the business’ needs.
It is important to consult stakeholders about what they hope to achieve with the app. You can use SMART objectives to measure its future success. Perhaps you are creating new organization software for employees. Your hypothetical aim might be to increase productivity.
By holding collaborative meetings, the business can work together to identify what they want to achieve. This will allow them to find out what they should be looking for. They might also brainstorm the design and “personality” of the app, considering factors such as what format it will be in and what operating system it will work on. Once they know these requirements, the app is ready to be developed.
2. Development of the product

Developers can now bring the proposed app to life. Research shows that 99% of mobile app startups fail. This reveals that the development process is crucial when it comes to the success of the app.
Development often involves coding and moving the app from an idea into the virtual world. The app will need to be created within the realms of what is possible.
There are some coding apps out there for beginners, but bringing your vision to life in the most effective way will usually involve consulting or employing specialists. They will utilize various methods, such as using wireframes to develop the software.
For internal software, development will involve coding – but not in the same way. Customer-targeted apps are often created for mobile devices. Meanwhile, internal apps will likely be for company hardware such as computers.
To stay ahead of the curve, you must choose the right team for the job, with your design being simple and intuitive.
3. Testing and quality assurance
Now it is time to review the app. Does it meet quality standards? Does it fulfill the requirements outlined at the start? This step can involve many extra employees, including quality assurance engineers and testers. They will have the knowledge required to ensure the app is ready and as error-proof as can be.
Continuous testing comes later on. If you are looking for a continuous testing definition, look no further. It is the conduction of constant automated tests designed to evaluate an app and its risks. It is somewhat normal to discover bugs down the line, but being as thorough as possible at this point will save time and money.
Testing is important, as your app will likely need to compete with similar apps on the market. Errors or bugs will frustrate customers and discourage use. Walkthroughs and reviews of the app can help with testing, and focus groups of potential customers should try out the app before release.
This step may prove to be the most time-consuming. Care should be taken to ensure there are as few bugs as possible.

4. Deployment
When the app is ready and free from errors, it can be released. Around 198,100 Android apps were added to the Google Play store in the first two months of 2021. This means businesses are in good company when it comes to customer releases. It also means there is a lot of competition.
Businesses should time their deployment accordingly. Avoid dates when direct competitors are likely to release their apps. The business may also need to consider other factors related to the release, such as producing marketing materials and anticipating increased demand.
To prepare for release, the app or software needs to be configured for the relevant platform. You must also release the app in the right way. Do not unveil internal software until employees have been properly trained in its use and have had the opportunity to familiarize themselves with the coming changes.
5. Continuous maintenance and improvements
The app must now be constantly reviewed and updated to get rid of bugs and to add new features as and when necessary.
This is an ongoing process. It will continue until the app is no longer useful and is discontinued. This could take anywhere from months to years. The team should focus on maintenance and errors that might affect its usage.
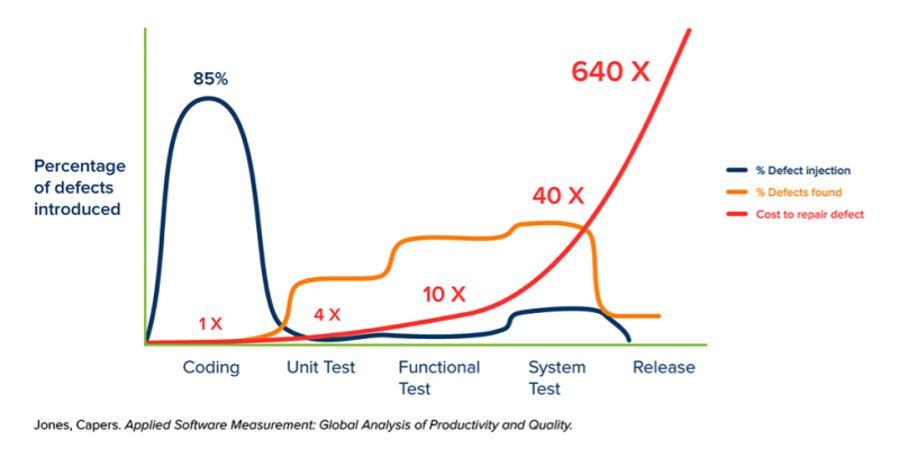
It is best to “shift left” and remove bugs and errors sooner rather than later, as this reduces costs in the long term. The above graph shows that removing bugs after release and beyond can increase costs by 640 times.
Shifting left is integral to ALM. It is a process of constant improvement and involves conducting tasks as soon as possible. Maintenance is also important. Carry out scheduled maintenance and manage the addition of new features to maintain top app performance.
Continuous testing will make your app stronger and ensure errors are resolved quickly.
The Benefits of ALM
Now that we have reviewed how ALM works and covered its five most important steps, it is time to consider its benefits.
Less downtime
One benefit is that the app will be consistently updated, meaning there is no need to wait between processes. This makes creation, release, and ongoing app management more efficient. The software testing methods that are part of ALM help with this.
Downtime is bad news for a business. Other competitors in your field may be plowing ahead, so having significant lapses where operations cannot take place will mean you get left behind.
Less downtime will save you money, as it will leave your business free to put its most important resources – i.e. its employees – to good use. In 2020, 25% of respondents worldwide stated that the average cost per hour of downtime was between USD 301,000 and USD 400,000.
Improve customer service
The preventative ideology of ALM keeps your app working for its users too. Any possible future downtime is resolved before it can even begin. This advantage is only for external apps, but this chart reveals how much customers value things working the first time. In all categories, the desire for a straightforward, informative answer is present. We can apply this to an app designed for their usage.
Notably, 12% of global respondents value being able to locate information without needing to contact the customer service team. This is something the business can address via its app.
An app that does not work in the way it should, or has bugs, will cause customer dissatisfaction. Customers may feel they need to contact the customer service team. This will make them much less likely to want to use the app, which may negatively impact the business’ objectives.
Happier employees
When it comes to internal software, employee satisfaction will improve thanks to ALM. This works in parallel with customer satisfaction above and is due to a combination of better visibility, better relationships, and less stress due to improved management.
Employee productivity will also increase. Workers will feel the comfort of having access to the results of ALM. This includes the internal software produced, which will aid productivity and organization.
Now back to external apps. Something that will help employees is knowing the part they must play in app development. With prior management systems, there may be confusion related to their role. With ALM, which includes all departments simultaneously, they will feel included.
This is particularly pertinent in current times. Many employees are currently working from home. The use of video conferencing tools has become normal, but professionals can still feel as though they are not part of the action. ALM resolves this.
Overcoming challenges in advance (i.e. better decision-making)
Most app-related challenges will be foreseeable with ALM. This is thanks to its adaptable and continuous improvement model. This puts the business in a position to make the necessary changes in advance.
Having this foresight makes it easier to plan for the future. Companies can make informed decisions that are good for the business. The business can quell any difficulties that might arise with the app during the continuous improvement stage, becoming immediately aware of problems. The constant reviews will afford sufficient time to address these issues.
This is only one step in the decision-making process, which also includes a review at the end to ensure the right decision was made. Yet it is arguably the most important, as it provides the key to effective decision-making from the outset.
Better visibility for all in the business
With a more linear model, tasks pass through a chain of command, yet ALM allows each department to have full visibility as they constantly work on the app over time. Employees will appreciate this transparency. They will know exactly what needs to take place and when, making them better prepared for the action ahead.
With ALM, everyone is more aware of the processes in the business. This creates a culture of inclusivity and a sense of security among workers. When employees believe they are part of a drive for change, they feel more valued and are likely to be more productive.
Improved collaboration and efficient communication between business and IT
There is another advantage of ALM: improving the relationship between the company’s central operations and its IT team. This results in increased productivity and efficiency. Furthermore, there may be future benefits for other projects between these two.
Many businesses are discovering the importance of IT as a central part of their operations. This is a trend that will guide how businesses work in the future. It can aid in making decisions related to important business–IT topics. This includes when to automate your testing, for example.
In fact, Bloomberg reported that collaboration is crucial to digital transformation in a business. The technological revolution is the reason for this shift in business practice. Companies are now working with the new functionalities available to improve their services.
The way ALM achieves this is via its constant development over time, necessitating that the two teams work closely together.

Next Steps
ALM, as a system, can unlock a variety of benefits for businesses. It can aid them in becoming more agile and better prepared for changes. It can help them to create a quality culture within their organization.
As explained above, ALM is a system that appears complicated at first glance, but in reality, it is pretty simple. Yet it goes without saying that workers must have proficient experience and skills to make app lifecycle management successful. Many different parts of ALM require attention and expertise.
Author’s Bio: Emily Rollwitz is a Content Marketing Executive at Global App Testing, a remote and on-demand app testing company helping top app teams boost their app retention rate, anywhere in the world. She has 5 years of experience as a marketer, spearheading lead generation campaigns and events that propel top-notch brand performance. Handling marketing of various brands, Emily has also developed a great pulse in creating fresh and engaging content. You can find her on LinkedIn.
Leave a Reply