Last Updated on December 15, 2023

The mobile device management (MDM) solution has revolutionized the landscape of several industries and, simultaneously, facilitated the digital transformation process. It is also an ideal tool to prevent data breaches and leaks if proper MDM security policies are put in place.
So, the first question you might have in mind is:
What is an MDM policy?
To put it simply, Mobile device management (MDM) policy is a set of compliance rules that can be implemented on corporate devices. It allows IT professionals to monitor, control, and manage mobile devices in a more organized and productive way.
More importantly, companies can add security measures to their policies for data protection. They are usually restrictions ranging from mandatory user authentication to limitations on using unauthorized applications or device functionalities. Such policies can effectively protect business data from potential danger and let mobile devices and applications run in a safe environment.
Yet, before you set out to create your own security policies, the first step is to fully understand the importance of MDM policy implementation.
Why do businesses need an MDM policy?
Since mobile devices have become ubiquitous in the workplace, today’s employees mostly use smartphones and tablets to tackle their day-to-day jobs. According to Statista, mobile workers in the US alone are expected to grow to 93.5 million by 2024 – nearly 60% of the total workforce.
This phenomenon poses an enormous security threat to organizations if the mobile devices – whether they are personal or company-owned – stay unmanaged. In fact, up to 67% of IT and IT security personnel – mainly from the US and Europe – confirmed that remote work with personal mobile devices has negatively affected their organization’s data security.
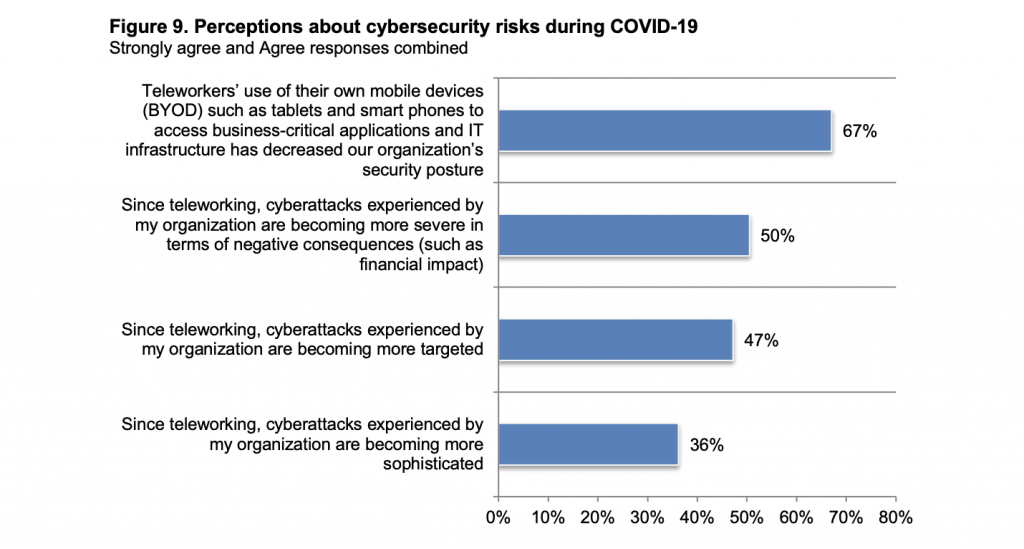
Some of the common violations include deliberate or unintentional data leaks, lost or stolen devices, and misuse of corporate resources. Employees might share confidential information and sensitive data with outsiders, install unauthorized apps for non-work purposes, and download files from unknown sources on corporate devices.
The truth is, just one of these little breaches is enough to pose an enormous threat to an organization’s cybersecurity, as it can potentially create a crack on the firewall that allows hackers to slip in. It might also lead to legal issues that can cost the company a fortune.
For example, in the healthcare industry, sharing a patient’s private information with unauthorized users via text message or social media is an obvious violation of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It can result in legal and financial ramifications.
On top of it, given how the device technology evolves constantly and rapidly at all times, enterprise IT will likely have a hard time trying to handle this overwhelming job of safeguarding corporate data without a robust MDM policy.

Step-by-step guide to creating & implementing an effective MDM policy
There are many guidelines on MDM policy settings that aim to help IT departments draw up a set of comprehensive rules for data protection. However, it can be quite difficult and intimidating to digest piles of information and put them into practice – not to mention the need to customize the restrictions for your workforce.
The instruction below aims to help you cut through the noise by focusing on the five most essential steps you can easily understand and follow.
1. Establish what devices should be used in MDM policies
There are various mobile devices on the market, but not all of them are suitable for accessing business data. Most companies approve tablets, smartphones, and laptops because they are more secure and easily managed than other electronic tools such as gaming gadgets, smartwatches, and media devices (e.g., MP3 players). Your enterprise may also decide whether it should offer corporate-owned equipment or adopt a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy.
2. Define the device approval process
After your enterprise selects what types of device employees can use, it is time to enforce the ground rules – how a mobile device is going to be approved for work. You should define the right model of a so-called corporate device by asking these questions: Is the device running the correct operating system? Does it include applications or data that imply some degree of insecurity? This approval process plays a key role in MDM policies as it is considered the first line of defense for cybersecurity.
3. Design security practices
Ways to secure a fleet of mobile devices can vary, depending on each company’s requirements and circumstances. But the general idea remains the same: to keep security threats away and avoid any data-leaking incidents. So, your company should watch out for unsecured networks, shady applications, and shadow IT usage. Additionally, mandatory installation of a security application on all corporate devices is strongly recommended.
4. Assign responsibilities to employees
No matter how flawless an MDM policy is, it can only work best when a company and its employees are on the same page. Once your company entrusts mobile devices to the workers, it should make sure they are aware of the risks of data breaches while performing business tasks outside the office. To enforce responsibilities to employees, companies can educate them on appropriate data usage and place restrictions on device access to applications, websites, or unknown networks.
5. Review your policies regularly
Once all is set, IT admins should never forget to make a plan to review their MDM policy regularly. It is a step often neglected but essential because a security policy can easily be outdated due to the constant advancement of mobile technology. Keep your policy settings up to date, and never forget to educate or re-train your employees on the new changes.
Now that you understand the process of creating an MDM policy, it is time to empower it with some valuable tools. As an MDM solution provider, AirDroid Business can help enterprises set up multiple security policies and categorize enrolled devices into different groups with predesigned settings.
To further extend your MDM capability, AirDroid Business also offers:
- Two-step authentication (2FA) and advanced data encryption
- Single app & multi-app kiosk mode to prevent misuse of devices
- Flexible enrollment options including quick installation for myriad devices
- Full visibility of device vitals and location tracking
- Real-time device monitoring through data usage reports
If you have any problems setting up policies, click here to find helpful resources as needed.
The 7 best practices for an MDM security policy
When using MDM platforms like AirDroid Business to set up security policies for mobile devices, enterprises often get confused about what rules and features they should include in order to effectively seal off vulnerabilities. Here are seven best practices, regardless of industry and size, that your company should consider adopting into your MDM strategy.
- Detailed reporting
Knowledge is power. If your business wants to effectively guard against cyber attacks, it is better to keep track of information related to devices and their users. By recording it as a detailed report, companies are more likely to spot the problem right after security threats come up.
However, keep in mind that the acts of collecting and storing data often raise privacy concerns, so you should always inform your employees and reach an agreement before any data compilation.
If you wonder what kind of data is available or suggested for recordkeeping, here are some recommendations: relevant accounts, networks, apps used on work devices and accounts, attacks, and vulnerabilities.
- Enforced Security Authentication
Identity and access management is a fundamental element in MDM policies, as no organization would like to see an uninvited guest accessing their back-end system without any hurdles.
To keep out hackers and unknown users, imposing mandatory password policies – such as lock screen passwords and secure passcodes – is a must-have.
Your company can consider using two-factor authentication (2FA) or ask IT departments to issue guidelines such as prohibiting password sharing, using automated password generators to enhance complexity, and setting minimum and maximum password age or limited login time.

- Controlled Updates
Outdated software and operating systems (OS) can create exploitable holes in cybersecurity that are deemed extremely vulnerable in the eyes of hackers. So, it is crucial to regularly patch up a bug or flaw by upgrading the software, applications, or OS as a reliable security strategy.
With suitable MDM tools in place, enterprises can easily impose a patch management strategy without worrying about any possible negligence or untimely updates. For instance, by using AirDroid Business, companies can execute, postpone, or customize updates that meet their needs. It helps to reduce business interruptions and data loss, allowing the system to run in a relatively stable status.
- Device Security Restrictions
Aside from passwords, there are many other methods to further secure mobile devices in the workplace. Since employees often use mobile devices out of sight, it is necessary for IT professionals to restrict device access to certain applications and websites.
Some common restrictions include application blocklists, app installation restrictions from unknown sources, disabling factory reset functions to ensure device compliance, and prohibiting connection to public WiFi. Your company can apply more than one rule at the same time and make various combinations depending on your requirements.

- Application Data Loss Prevention Policy
Regardless of scale and industry, every organization needs a data loss prevention (DLP) policy to avoid data stored in lost devices being stolen or deleted. This is especially true when it comes to confidential and sensitive data such as medical records, financial documents, and intellectual property.
The best solutions to prevent data loss when a device is lost or stolen are prohibiting users from sharing data or documents to personal devices through USB file transfer or to external USB devices. Also, your company should be able to wipe out specific app data remotely under such circumstances to avoid data leakage.
- Anti-malware software Installation
This is a basic yet often underrated practice that your company should definitely pay attention to. In a digital world full of phishing emails, ransomware, and malware – antivirus software is an essential tool to fight against cybercrime.
An effective antivirus program is able to carefully screen incoming data, look for signs of malicious attempts, and block threats before they reach your devices.
It is imperative for IT admins to make the installation of an anti-malware application mandatory so that every enrolled device will automatically have the right protection to run in optimum conditions.

- Penetration Testing
Pen testing, short for penetration testing, is a process of ethical hacking that allows cybersecurity engineers or penetration testers to simulate an attack on your corporate’s digital systems and assets.
In doing so, they can have a close look at how and where real hackers might get in or past the defenses. Then, their mission is to patch up the possible security holes that have been found in the process. This way, problems are fixed specifically and accurately; plus, it enhances the chance for security staff to outsmart hackers and continually strengthens protection for corporate devices.
How will different industries benefit from an MDM policy?
IT departments and managed service providers (MSPs) can work more efficiently using predefined policies to quickly set up and manage new devices. By enforcing WiFi, language, time zone, APN, and other settings, devices can run in a specific environment that the company wants to build.
Since medical institutions use mobile devices to store personal data of patients’ medical records and prescription history, they can implement an MDM security policy to enable lock screen passwords and restrict USB connections to prevent data loss.
Having to manage a fleet of mobile devices used by drivers, logistics and transportation industries can create a blocklist for websites and apps in MDM policies, allowing only approved apps to be downloaded and operated. It helps to avoid data breaches and detect device usage irrelevant to work purposes.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, highly effective MDM policies should always retain a high level of cybersecurity. If your company is about to invest in or extend the functions of an MDM tool, remember that mobile device security should never be compromised, and you should always incorporate robust data protection measures into your IT infrastructure.
